Solving Choking While Sleeping
Choking while sleeping, snoring, and other nighttime disturbances may seem like trivial issues, but they can have a significant impact on your health and well-being. These nighttime disturbances may be indications of underlying sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea, which require prompt attention and treatment. Addressing these issues is crucial not only for a good night’s rest but also for maintaining overall health and preventing serious complications. Take a journey with us as we explore the connection between choking while sleeping, snoring, and other sleep-related problems, learn to identify the symptoms of sleep apnea, adopt lifestyle changes to alleviate these issues, and examine various medical treatments that can help you breathe easier and sleep better at night.
Key Takeaways
Understanding choking and snoring during sleep can help identify potential sleep disorders. Lifestyle changes, such as weight management and avoiding alcohol/sedatives, may reduce the risk of choking & snoring. Professional medical treatment is essential to accurately diagnose & treat obstructive sleep apnea in children.
Understanding Choking and Snoring During Sleep
Choking and snoring during sleep may be more than just annoying nighttime nuisances. They can be symptoms of sleep disorders like sleep apnea, which is characterized by interrupted breathing during sleep. Sleep apnea can lead to a host of health problems, including high blood pressure, heart disease, and excessive daytime sleepiness. Grasping the link between choking and snoring during sleep aids in pinpointing potential sleep disorders and pursuing the right treatment. Recognizing sleep apnea symptoms can guide you towards better sleep quality and overall health improvement.
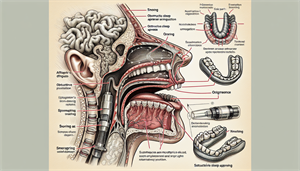
The Mechanics of Snoring
Snoring occurs when the flow of air through the mouth and nose is partially blocked during sleep. This blockage causes the soft tissues in the throat, such as the soft palate and other tissues in the mouth, nose, or throat, to vibrate against each other, producing the characteristic snoring sound. Various factors can lead to snoring, including: Obesity, Alcohol consumption, Sleeping on one’s back, Nasal congestion. The anatomy of the mouth, throat, and sinuses Reduced muscle tone in the upper airways during sleep can also contribute to snoring. When the muscles in the throat and mouth become too relaxed, they can obstruct the airway, leading to turbulent airflow and vibrations that manifest as snoring. Grasping snoring mechanics aids in identifying potential sleep disorders more effectively and implementing suitable lifestyle adjustments or treatments.
Choking: A Symptom of Sleep Apnea
Choking during sleep can be a symptom of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, a sleep disorder characterized by interrupted breathing during sleep, also known as sleep disordered breathing. Sleep apnea can be classified into two main types: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) Central sleep apnea (CSA) OSA occurs when the muscles and soft tissues in the throat collapse and obstruct the airway, while CSA happens when the brain fails to send proper signals to control breathing. The most prevalent indication of sleep apnea is episodes of choking while asleep, often accompanied by loud snoring, gasping, or producing other atypical noises. Sleep apnea is associated with various risk factors, including obesity, advanced age, male gender, large neck circumference, and certain medical conditions such as hypertension. Untreated severe sleep apnea can lead to serious health complications for sleep apnea sufferers, such as high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, obesity, Alzheimer’s, and GERD.
Identifying Sleep Apnea-Related Choking
Detecting sleep apnea-related choking is key for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Symptoms such as loud snoring, gasping for air, and frequent awakenings c