What Are the Warning Signs of Sleep Apnea?
Sleep Apnea, a commonly underestimated sleep disorder, presents a unique challenge to both its sufferers and medical professionals. It’s like a stealthy night prowler, often going unnoticed and undiagnosed, yet leaving a trail of exhaustion, frustration, and health issues. But what if you could spot this prowler before it wreaks havoc on your health?
Understanding “what are the warning signs of sleep apnea”, health consequences, risk factors, and treatment options for sleep apnea could be your first step towards reclaiming restful nights and energetic days.
Key Takeaways
-
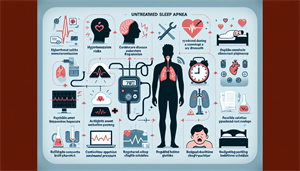
Sleep apnea is characterized by symptoms such as loud snoring, disrupted breathing during sleep, excessive daytime fatigue, and morning headaches, which can severely impact one’s quality of sleep and overall health.
-
Untreated sleep apnea can lead to serious health consequences including cardiovascular issues, hypertension, metabolic disorders like type 2 diabetes, and mental health problems such as depression and cognitive impairment.
-
Treatments for sleep apnea include the use of CPAP machines, which are considered the gold standard, as well as alternative therapies, surgical interventions, and lifestyle changes such as weight loss and improving sleep hygiene.
Unveiling the Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
Understanding sleep apnea’s common indicators is a crucial step in combating it. Sleep apnea often manifests in: Loud snoring, Disrupted breathing during sleep, Gasping for air and disrupting sleep rhythm,
Excessive tiredness during the day, even after a full night’s rest, Morning headaches, a silent warning sign that sleep patterns have been disrupted due to interrupted breathing.
These are just a few warning signs, or tell-tale symptoms of sleep apnea. However, a deeper understanding of these symptoms is necessary.
Interrupted Breathing: More Than Just Snoring
While snoring often becomes the brunt of jokes, it can signal a serious issue. Sleep apnea is not just about loud snoring; it involves a complex interplay of disrupted breathing patterns.
Obstructive sleep apnea, one of the two primary classifications of the condition, can lead to sleep apnea snores, which are caused by: a narrowing or complete closure of the airway due to the relaxation of throat muscles, lower oxygen levels in the blood, brief awakenings to reopen the airway, leading to disrupted sleep. This leads to sleep interruption, depriving you of the deep, restorative sleep stages necessary for high-quality rest.
Daytime Fatigue Despite a Full Night's Rest
A common misconception about sleep apnea is that if you sleep through the night, you’re safe. The reality is, even after a full night’s sleep, individuals with sleep apnea often experience: Daytime fatigue, Severe daytime drowsiness, Fatigue, Irritability.
These symptoms result from repeated pauses in breathing, known as apneas, which prevent individuals from reaching deeper, restorative stages of sleep. These awakenings affect daily functioning and performance. Therefore, if you’re experiencing excessive daytime sleepiness despite a full night’s rest, it could indicate a battle with sleep apnea.
Waking Up with a Start: Gasping and Choking at Night
Imagine being jolted awake in the middle of the night, gasping or choking for air. This can be a reality for individuals suffering from sleep apnea, including central sleep apnea. The obstruction or collapse of the upper airway during sleep leads to reduced oxygen and increased carbon dioxide levels in the body, prompting the brain to awaken the individual to resume normal breathing.
The brain is typically responsible for maintaining steady breathing during sleep, but in cases of sleep apnea, airway collapse can result in breathing interruptions and symptoms such as gasping or choking. Such episodes can be evaluated using the Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI), which tallies the number of breathing interruptions per hour of sleep.