What is the Best Sleep Position for Sleep Apnea?
Imagine finally getting a good night’s sleep, free from the constant disruptions caused by sleep apnea. What if the key to achieving that rested feeling lies in the way you sleep? Understanding the relationship between the best sleep position for sleep apnea and this common sleep disorder can be a game-changer for those seeking relief.
Key Takeaways
Side sleeping is the optimal position for sleep apnea sufferers, while back sleeping should be avoided. Pillows and positional therapy devices can help to maintain an appropriate sleep position. Healthy lifestyle modifications and CPAP therapy are additional management techniques used to improve overall sleep quality.
The Impact of Sleep Positions on Sleep Apnea
The position in which you sleep can significantly impact the severity of your sleep apnea symptoms. For some, a simple change in sleeping position can make all the difference in reducing the frequency of apnea episodes and improving overall sleep quality. However, not all sleeping positions are created equal when it comes to sleep apnea management. The following discussion will focus on identifying beneficial and harmful sleep positions for individuals with sleep apnea. Additionally, we will provide tips on maintaining an ideal sleep position for improved sleep quality.
Side Sleeping: The Optimal Position
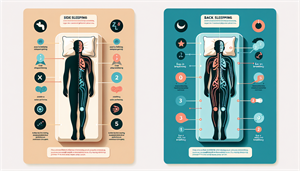
Side sleeping is considered the best position for those with sleep apnea. This position counteracts the gravitational force that may cause the tongue and tissues to block the airway, making it one of the best positions for sleep apnea. In particular, sleeping on the right side can reduce snoring and facilitate better blood flow, contributing to a good night’s sleep. For the most benefits from side sleeping, remain extended rather than curling up, to prevent complications like acid reflux. For those using a CPAP machine, side sleeping may enable a reduction in air pressure, as this position facilitates easier breathing. Therefore, trying side sleeping might be beneficial if you’re grappling with sleep apnea.
Stomach Sleeping: A Controversial Option
The topic of stomach sleeping for sleep apnea sufferers is a debated one. Some studies have demonstrated benefits, such as a 2019 study revealing that sleeping in a prone position could benefit individuals with mild sleep apnea. However, stomach sleeping can also cause neck strain and may impede the use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) devices, which are frequently utilized for sleep apnea treatment. If you choose to sleep on your stomach, turn your head to the side to allow room for breathing, and use a thin pillow under the pelvis and abdomen to prevent hyperextending the neck. As always, consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best sleep position for your individual circumstances.
Back Sleeping: The Worst Position
Back sleeping is the least recommended position for sleep apnea patients. Gravity exerts a downward pull on the tongue and throat tissues, resulting in airway obstruction. This position can exacerbate symptoms, especially for those with moderate sleep apnea. To reduce the adverse impacts of back sleeping, you can:
- Utilize a firm mattress
- Abstain from using pillows
- Elevate the head with a wedge pillow
- Turn the head slightly to the side
- Use a small pillow to maintain the turned head position
These measures can assist in reducing the negative effects of sleeping on your back.
Strategies for Maintaining the Right Sleep Position
A consistent sleep position is key for those with sleep apnea who aim to improve their sleep quality and lessen symptoms. The subsequent discussion will cover numerous strategies to maintain an ideal sleep position. These include using supportive pillows, positional therapy devices, and creating a comfortable and well-aligned sleep environment. Using supportive pillows can